
In order to diagnose deep vein thrombosis, your doctor will ask you about a few symptoms. A physical exam will also be conducted to check the swollen areas, tenderness or discoloration of your skin. On the basis of how likely you will be having a blood clot, you will be suggested some tests like:
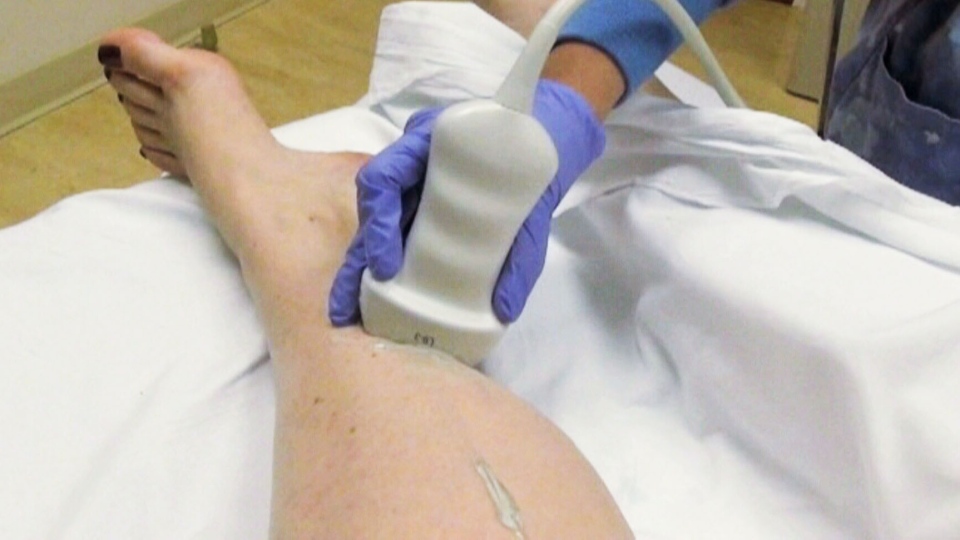
- Ultrasound: a transducer is placed over a body part where there is a clot that sends sound waves to the affected area. As the waves travel via your tissue and reflect back, the computer translates the waves into a moving image on a video screen. You might also see the clot in the image. Many times, a series of ultrasounds are conducted over several days to ascertain if a blood clot is growing or is there any new one.
- Blood test: the person with high DVT has an extra amount of substance in the blood called D Dimer.
- Venography: in this, a dye is injected into a large vein placed on your foot or ankle. An x ray makes an image of those veins and seek the clots. But usually ultrasound is the easiest way to confirm the diagnosis.
- CTI or MRI scans: both are helpful in creating visual images of your veins and proves that you have a clot.
Treatment
DVT is aimed at avoiding the clot from increasing in size and breaking it loose and causing a pulmonary embolism. Then the next gist is to reduce the chances for it to happen again. Deep vein thrombosis treatment entails:
- Blood thinners: DVT is treated with anticoagulants or blood thinners. They can be injected or taken as pills that can reduce the chances of clot to take place. They don’t break up the current blood clots and prevent them to increase in size and ever developing again. If injecting, do it under the skin or into your arm vein. The latter is applicable for heparin. Take this as your doctor prescribes as overdosing or under-dosing it can cause grave side effects. This is simply not valid for pregnant women.

- Clot busters: if your DVT or pulmonary embolism is serious, then your doctor may prescribe drugs that segregates the clots or named as clot busters or thrombolytics. These drugs are given via an IV line to segregate the blood clots or via a catheter placed into the clot directly. They may also cause serious bleeding, so they are only valid for those who have severe blood clots.
What is your reaction?
Excited
0
Happy
0
In Love
0
Not Sure
0
Silly
0











